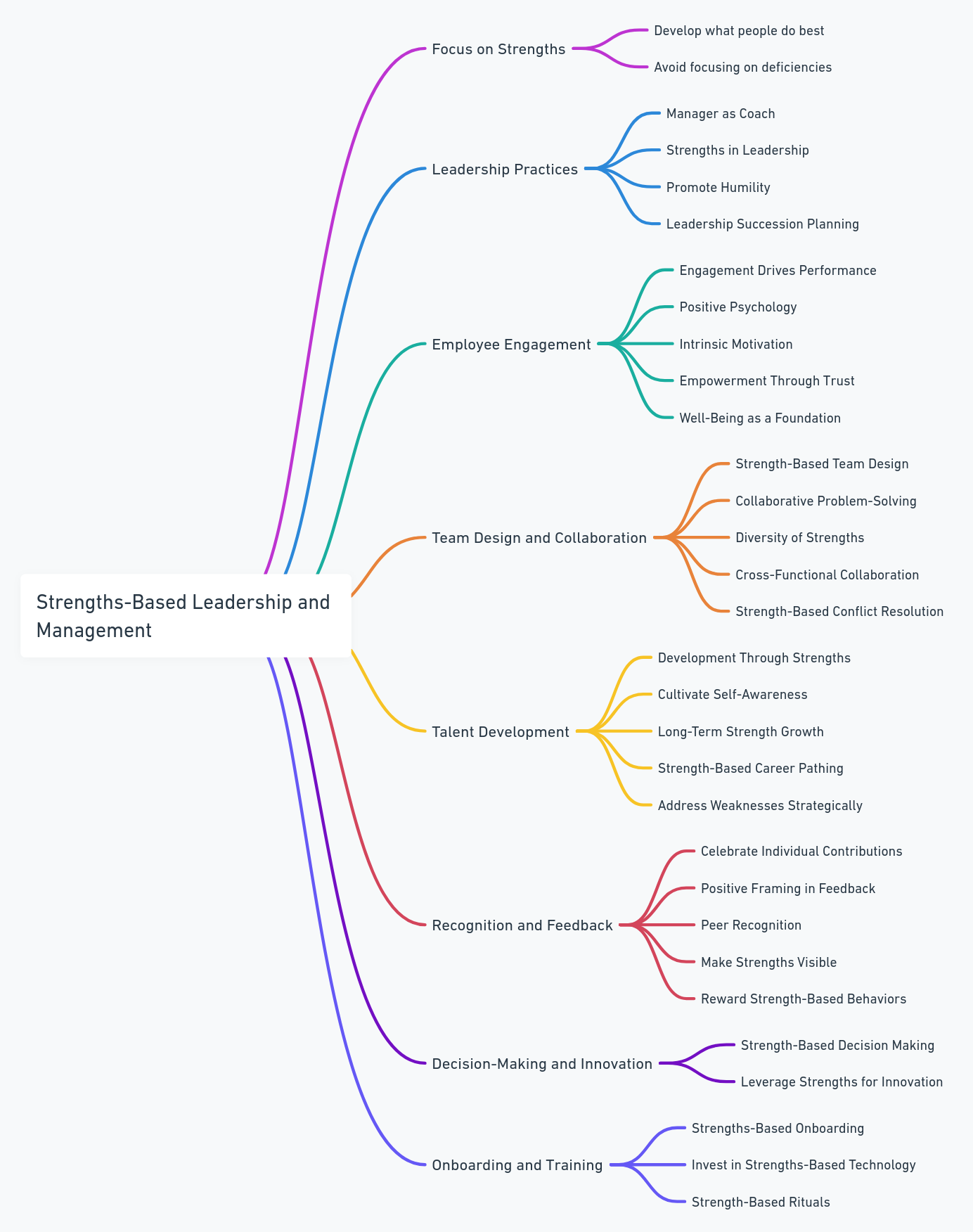
The Top 52 Strengths-Based Leadership Principles
If you find this tool helpful, consider showing your support: Buy Me A Coffee.
1. Focus on Strengths, Not Weaknesses
• Strengths-Based: Develop what people do best.
• Conventional Wisdom: Focus on fixing deficiencies.
2. Individualization Over Standardization
• Strengths-Based: Tailor work to each person’s unique strengths.
• Conventional: Apply uniform rules and job descriptions.
3. Engagement Drives Performance
• Strengths-Based: Align strengths with roles to maximize engagement.
• Conventional: Engagement is a byproduct of results.
4. Development Through Strengths
• Strengths-Based: Help employees grow their natural talents.
• Conventional: Focus training on filling skill gaps.
5. Collaborative Problem-Solving
• Strengths-Based: Build teams where strengths cover weaknesses.
• Conventional: Emphasize individual problem-solving.
6. Positive Psychology
• Strengths-Based: Highlight what’s working to inspire improvement.
• Conventional: Focus on what’s broken to fix issues.
7. Manager as Coach
• Strengths-Based: Managers guide and nurture growth.
• Conventional: Managers oversee tasks and enforce results.
8. Intrinsic Motivation
• Strengths-Based: Align tasks with passions and talents.
• Conventional: Use external rewards like promotions or bonuses.
9. Empowerment Through Trust
• Strengths-Based: Trust employees to succeed in their areas of strength.
• Conventional: Monitor closely to ensure compliance.
10. Diversity of Strengths
• Strengths-Based: Seek diverse strengths for team balance.
• Conventional: Focus on hiring for specific skills or experience.
11. Strengths in Leadership
• Strengths-Based: Leaders delegate tasks they are weak in.
• Conventional: Leaders are expected to be well-rounded in all areas.
12. Strength-Based Team Design
• Strengths-Based: Build teams with complementary strengths.
• Conventional: Assign teams based on availability or hierarchy.
13. Well-Being as a Foundation
• Strengths-Based: Invest in employee well-being to drive performance.
• Conventional: Well-being is secondary to results.
14. Celebrate Individual Contributions
• Strengths-Based: Recognize individuals’ unique strengths.
• Conventional: Reward based on standardized metrics.
15. Leverage Strengths for Innovation
• Strengths-Based: Use strengths to foster creativity and solve problems.
• Conventional: Rely on structured processes for innovation.
16. Cultivate Self-Awareness
• Strengths-Based: Encourage individuals to understand their talents.
• Conventional: Assume self-awareness comes with experience.
17. Positive Framing in Feedback
• Strengths-Based: Offer feedback as growth opportunities.
• Conventional: Emphasize mistakes and failures.
18. Learning from Success
• Strengths-Based: Analyze successful strategies to replicate them.
• Conventional: Focus primarily on analyzing failures.
19. Long-Term Strength Growth
• Strengths-Based: Develop talents over time for sustainability.
• Conventional: Prioritize quick skill development for immediate gains.
20. Engagement Through Autonomy
• Strengths-Based: Give freedom in areas of talent.
• Conventional: Control processes to ensure outcomes.
21. Energy Alignment
• Strengths-Based: Align work with activities that energize employees.
• Conventional: Assign tasks based on needs, not energy.
22. Success Through Relationships
• Strengths-Based: Build trust-based relationships to enhance team dynamics.
• Conventional: Relationships are secondary to tasks and goals.
23. Strength-Based Performance Metrics
• Strengths-Based: Measure performance by how well strengths are used.
• Conventional: Use standardized productivity metrics.
24. Proactive Career Pathing
• Strengths-Based: Map careers around individual strengths.
• Conventional: Career growth is dictated by organizational needs.
25. Strength-Based Leadership Culture
• Strengths-Based: Build an organization-wide strengths culture.
• Conventional: Culture evolves based on management styles.
26. Strengths-Driven Decision Making
• Strengths-Based: Decisions are informed by individual and team strengths.
• Conventional: Decisions rely on hierarchy or job titles.
27. Seek Complementary Partnerships
• Strengths-Based: Pair individuals whose strengths balance weaknesses.
• Conventional: Expect employees to manage their own deficits.
28. Assign Roles Based on Strengths
• Strengths-Based: Match employees to roles that amplify talents.
• Conventional: Assign based on job descriptions or seniority.
29. Resilience Through Strengths
• Strengths-Based: Use strengths to bounce back from setbacks.
• Conventional: Focus on problem-solving techniques.
30. Strengths-Based Conflict Resolution
• Strengths-Based: Leverage strengths to mediate and resolve disputes.
• Conventional: Rely on rigid policies to handle conflicts.
31. Recognize the Strengths of Introverts
• Strengths-Based: Value quiet but impactful contributions.
• Conventional: Reward more visible achievements.
32. Encourage Strengths in Creativity
• Strengths-Based: Foster innovation by using creative strengths.
• Conventional: Follow predetermined processes for creative output.
33. Talent-First Hiring
• Strengths-Based: Hire for strengths over experience alone.
• Conventional: Prioritize experience and qualifications.
34. Embrace Flexibility
• Strengths-Based: Adapt roles to align with strengths.
• Conventional: Expect employees to fit rigid roles.
35. Nurture Emotional Intelligence
• Strengths-Based: Develop empathy and relationship-building skills.
• Conventional: Treat emotional intelligence as secondary.
36. Align Strengths with Purpose
• Strengths-Based: Connect employees’ strengths to the organization’s mission.
• Conventional: Focus on immediate tasks rather than long-term purpose.
37. Create Strengths-Based Onboarding
• Strengths-Based: Begin with a focus on identifying and using strengths.
• Conventional: Focus onboarding on compliance and policy.
38. Build Psychological Safety
• Strengths-Based: Foster environments where people feel safe sharing strengths.
• Conventional: Assume employees will naturally feel comfortable.
39. Identify and Maximize Signature Strengths
• Strengths-Based: Focus on amplifying top strengths.
• Conventional: Expect employees to develop all-around skills.
40. Reward Strength-Based Behaviors
• Strengths-Based: Incentivize actions that leverage strengths.
• Conventional: Reward task completion regardless of method.
41. Encourage Peer Recognition
• Strengths-Based: Promote team members recognizing each other’s talents.
• Conventional: Recognition comes primarily from management.
42. Make Strengths Visible
• Strengths-Based: Share individual strengths publicly within teams.
• Conventional: Assume strengths will become evident over time.
43. Coach for Self-Discovery
• Strengths-Based: Guide employees to uncover their talents.
• Conventional: Direct employees based on organizational needs.
44. Reduce Strength-Draining Tasks
• Strengths-Based: Minimize tasks that don’t align with strengths.
• Conventional: Expect employees to manage all responsibilities equally.
45. Invest in Strengths-Based Technology
• Strengths-Based: Use tools to measure and optimize strengths.
• Conventional: Rely on general HR or performance tracking systems.
46. Evaluate Strengths at All Levels
• Strengths-Based: Apply this approach across leaders, teams, and individuals.
• Conventional: Focus strengths discussions on employees, not leaders.
47. Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration
• Strengths-Based: Enable collaboration by aligning strengths across functions.
• Conventional: Keep teams siloed by expertise.
48. Practice Humility
• Strengths-Based: Leaders acknowledge and rely on others’ strengths.
• Conventional: Leaders are expected to have all the answers.
49. Strengths-Oriented Succession Planning
• Strengths-Based: Select future leaders based on talents and strengths.
• Conventional: Succession planning relies on seniority or tenure.
50. Address Weaknesses Strategically
• Strengths-Based: Mitigate weaknesses with complementary strengths.
• Conventional: Focus on fixing weaknesses directly.
51. Leverage Employee Input
• Strengths-Based: Involve employees in shaping roles based on their strengths.
• Conventional: Roles are assigned based on management decisions.
52. Create Strength-Based Rituals
• Strengths-Based: Integrate strengths-based practices into daily routines.
• Conventional: Rituals focus on broad performance or compliance.